- The rise of digital banking: statistics
- Accenture’s report
- Investments in personalization: the market situation
- AI in banking: challenges and advantages
- What the concept of personalization in banking includes
- Personal consultation
- Virtual assistants
- Services ensuring client security
- How banks use personalized services
- Personalization services and Big Data
- Client-oriented approach
- Conclusion
The financial sector doesn’t stand apart from technological innovations. IT solutions are changing the ways we organize businesses and communicate with clients, streamlining our work. Among promising areas of such innovations in banking are financial software solutions for personalization. These marketing tools for banks offer advantages to both entrants like online banks and traditional financial institutions. FinTech experts from Andersen will share what makes the personalization trend relevant for the financial industry, what’s needed to develop personalization services, and why a client-oriented approach should replace traditional technologies for working with clients.
The rise of digital banking: statistics
Personalization services help the enterprise and the client to interact in such a way that the consumer receives a customized option for their interests and needs even in the case of automatic service operations. Why does it work? And how to achieve this?
According to research data, when using banking systems, people apply automatic services and give them access to their personal data more and more often. This improves the quality of services. The World Retail Banking Report 2021 by Capgemini states that 86% of retail banking consumers are willing to share their data to get a better and more personalized experience.
In 2020, Accenture conducted a survey of around 47,000 bank clients in 28 countries. According to its results, 54% of respondents want to have tools to monitor their budgets and make real-time spending adjustment decisions, and 41% of respondents are eager to seek computer-generated banking advice.
The study also found that more than half of bank clients interact with their services via mobile applications or special web services at least once a week. This is 18% higher than in 2018. Other data shows that about 77% of bank clients prefer to make purchases using credit or debit cards rather than cash. According to McKinsey, among the 40% of clients who use FinTech banking software services on a daily basis, nine out of ten are satisfied with the quality of service.
The rise of digital banking is largely driven by pandemic circumstances. In any case, according to a report by PYMNTS, more than 75% of bank clients plan to maintain their level of interaction with digital banking services at the current level in the future.
Accenture’s report
Accenture has divided all bank clients into four main categories according to their characteristics. These groups are:
- Pragmatists;
- Traditionalists who prefer live contact and avoid technological means of interaction;
- Pioneers - tech-savvy risk-lovers;
- Skeptics - tech-cautious clients who are usually unhappy with banking software services.
Notably, the personalization of banking services is welcomed even by 55% of traditionalist users. Among the largest group of users - skeptics - 80% of those surveyed agreed to permit the collection of their personal information in return for personalized banking services. At the same time, about 25% of the traditionalist group were the only respondents who actively opposed the introduction of personalization services in favor of keeping the live methods of communication between clients and the bank.
Accenture’s report emphasizes: “Personalized services should also demonstrate added value. It is not enough just to tell consumers how they are spending their money. Instead, providers should show them how they can save money and take advantage of offers.”
The study has shown that, over the pandemic period, client confidence in banking service providers dropped by a record-breaking 14%. However, this trend may change with the further efforts of the banking institutions. They only need to prioritize the demands of flexibility, technical innovation, and personalization of services.
The conservatism of users also affects the potential success of banks in their efforts to personalize services. This gives financial institutions time to reform their services. According to Bankrate’s study, bank clients have been using the same open account for on average 14 years, and a fifth have kept their account open for more than 20 years.
Investments in personalization: the market situation
Many banks are aware of the current market situation. According to research by the Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU) and Temenos, 77% of banking leaders consider AI tools as what separates winning from losing banks. Along with that, 66% of respondents are sure that such technologies as AI, the Cloud, and DevOps will become drivers of growth for the global banking sector in the next five years. This is reflected in the volume of investments.
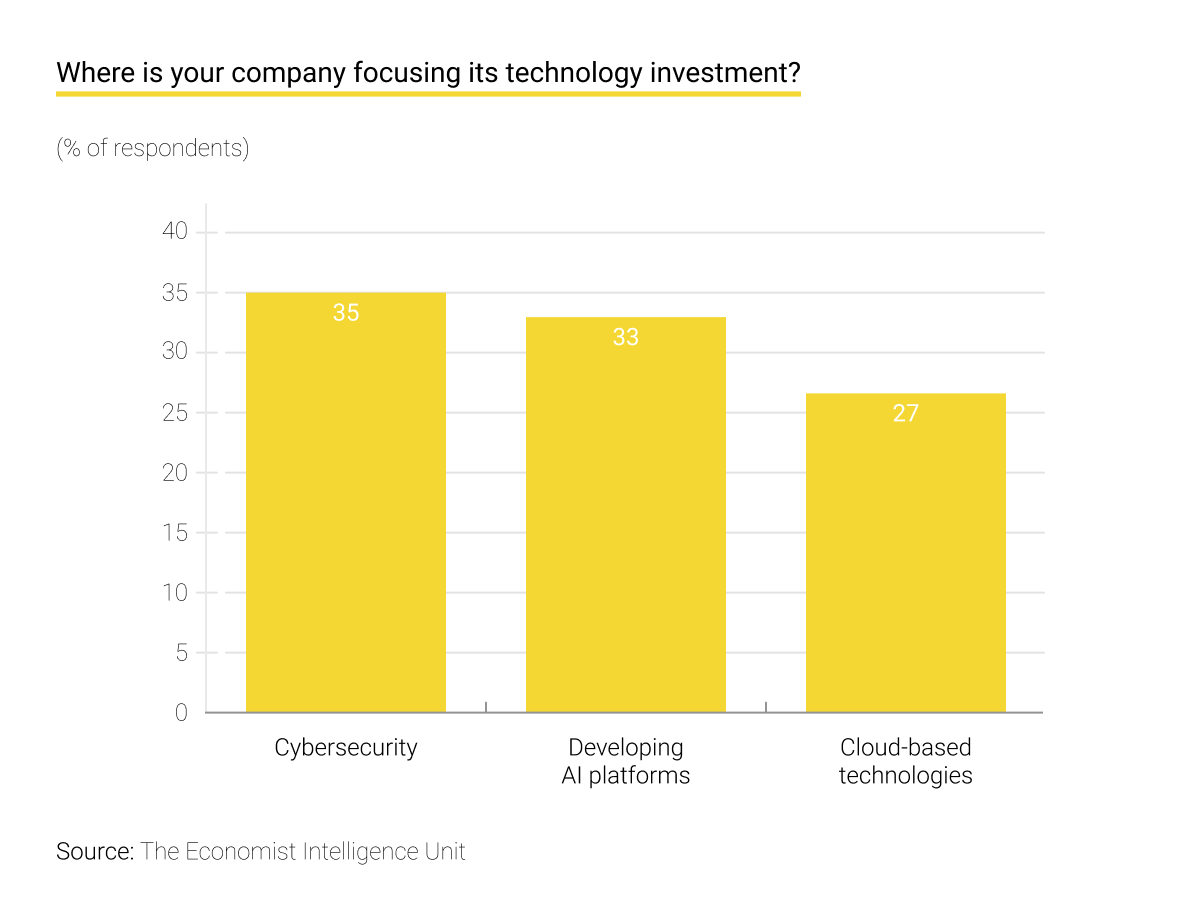
As for personalization, about half of banking leaders (45%) are focusing on building a digital ecosystem to improve client experience and revenue streams. Data from PwC says that 80% of banks have already realized the benefits of using AI in FinTech. This is especially true for security applications, personalized services, and improved internal operations.
AI in banking: challenges and advantages
The widespread use of AI tools raises the question about an ethical, fair, and transparent decision-making mechanism. Also, this raises the problem of overcoming the "black box" and of the ability of users and managers to delve into the work and recommendations of automated services.
Banks must take full responsibility for the decisions their AI-powered services make. This means that flaws in training systems and involuntary discrimination against users are unacceptable. The issue of collecting and storing users’ personal data is also topical. Banks' actions must comply with the requirements of legal regulations and not lead to breaches of personal security.
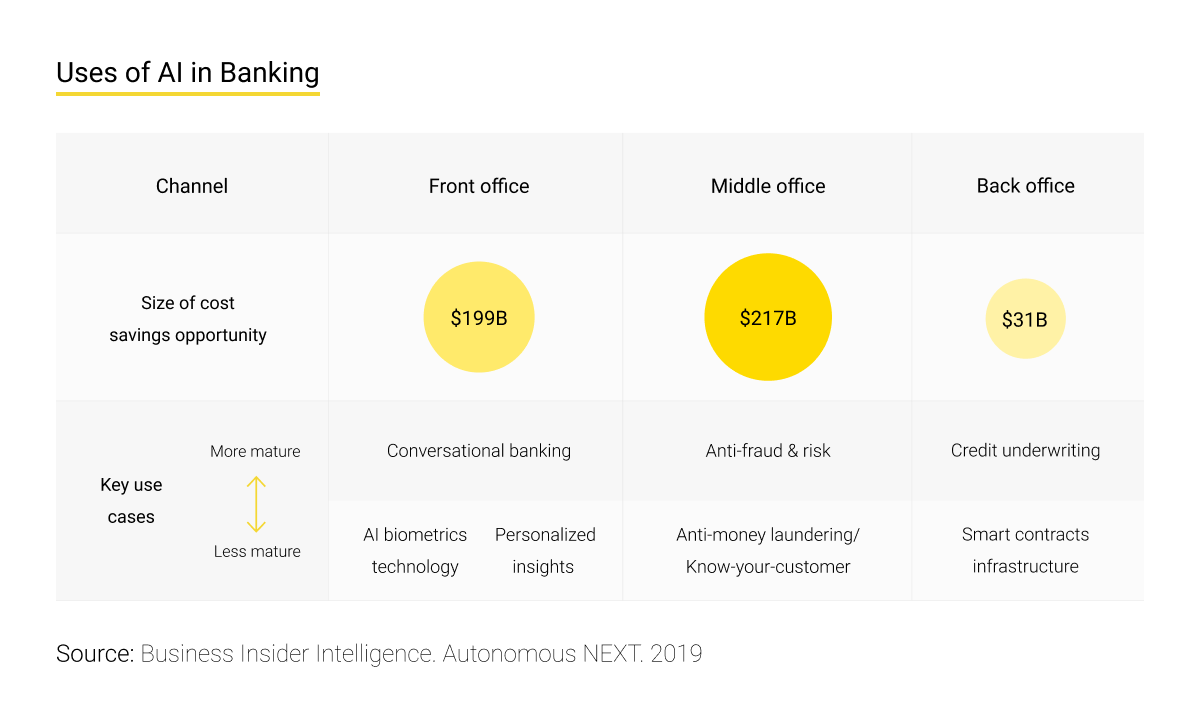
The benefits of personalization services are evident. According to the Business Insider Intelligence report of 2021, the use of AI for front-office will potentially save the banking industry about $199 billion by 2023.
Personalization creates a flexible environment for client-bank interactions, which affects the retail banking market. According to the report, AI tools provide banks with benefits at the middle-office and back-office levels too. This reflects in the correct risk assessment, decision-making on granting loans, next best offer analytics, and the improved security of the banking software system and personal accounts. Security is ensured by anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulatory checks.
About 84% of banking leaders consider proactive engagement and personalized guidance to be the key strategic goals for 2021, although some small financial institutions believe they don’t have sufficient tools for this.
What the concept of personalization in banking includes
BCG estimates that for every $100 billion of its assets, a bank can generate $300 million in profit enhancement by personalizing its interaction with clients.
Personalization implies that a financial institution knows its clients, understands their needs and wishes, and organizes all data to meet them. The latter means that the bank makes the right decisions in each particular case at the right time and through the right channel.
Personalization is sometimes confused with segmenting product offers, customizing homepage messages, and digitizing the customer journey, but these are just some of its components. Although not all clients see eye to eye about interacting with banking services, personalization helps banks gain their trust.
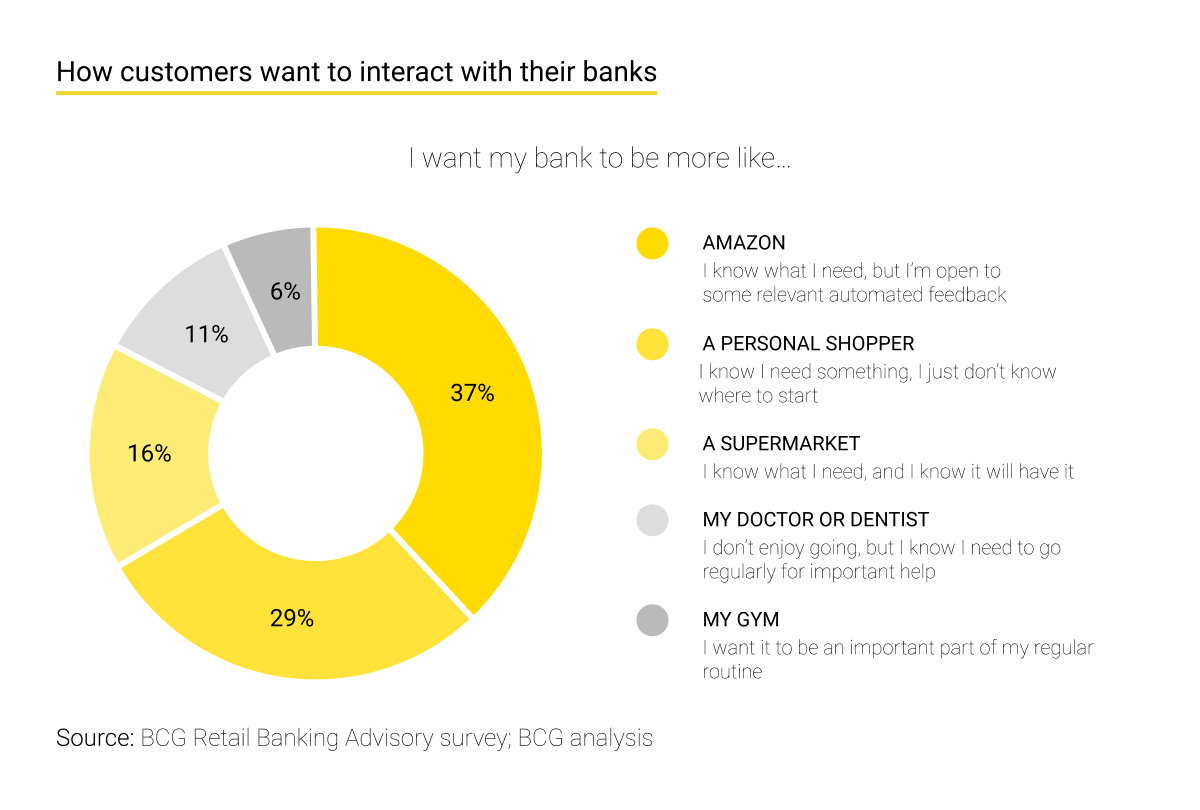
BCG’s experts emphasize: “To be sure, personalization in banking is not primarily about selling. It’s about providing service, information, and advice, often on a daily basis or even several times a day.”
What promising personalization services are demanded by both clients and banks?
Personal consultation
First and foremost, there is a demand for personal consultations using automated services. With their help, clients receive answers about their account status, terms of service, promotions, and offers round-the-clock. In fact, this is full-fledged individual support for a client, adapting to their frequent requests and providing detailed information without the need for human operators. It is essential that personalization is not limited to calling the client by their name but helps in better navigation through the banking system based on customized management settings and search history.
This service helps a client to more confidently interact with banking services via electronic communication channels. To organize it, conversational banking technology is often used. It primarily employs a digital communication channel and provides hyper-personalization of the service. This requires that the service provider develops NLU/NLP-based solutions for AI.
The system easily enters into communication with the client, recognizes them, and advises on a wide range of financial matters. It can often substitute for a specialized financial consultant. The result is the client's growing confidence in the banking system, which, according to the BAI’s December Executive Report, is fundamentally important for the financial sector.
Virtual assistants
Virtual assistants and robo-advisors are almost synonymous with personalized service. Their tasks are to constantly monitor the state of the client's wallet, ensure the absence of outstanding automatic payments, remind of transactions and transfers, maintain savings accounts, check authorization, and carry out other routine operations. Among the advantages of an automatic advisor are the ability to give recommendations on managing user accounts, generate suggestions for improving financial performance, give advice on high-yield investments, and carry out automated trading on online platforms based on the selected parameters.
For example, solutions such as the KAI conversational platform and the Abe AI virtual assistant combine the functions of a chatbot, financial manager, consultant, and virtual assistant and can be integrated with many services and mobile applications.
This service may also contain the function of a financial analyst and forecaster. The banking software system collects data about the state of the market and its development trends and, based on this, suggests recommendations to the client. In the future, this may lead to their substitution for corresponding specialists.
Similar financial software solutions can also sound the alarm in the event of an acute decrease of the balance and recommend additional investment in a profitable enterprise. For example, Trim proactively takes care of the client's financial well-being and helps them reduce their costs.
According to data by Deloitte, automatic robo-advisors are already managing assets of $3 trillion. This figure is expected to reach $16 trillion by 2025, especially through the expansion of personalization services.
Consulting and analytics strategy personalization depends on many factors, such as the age and gender of a client. Many financial institutions are now focusing on millennials, as they comprise the majority of the working-age population and are about to receive a significant share of the inherited wealth. This generation is more tech-savvy, has more trust in digital systems, actively uses mobile banking, and is ready for financial service personalization.
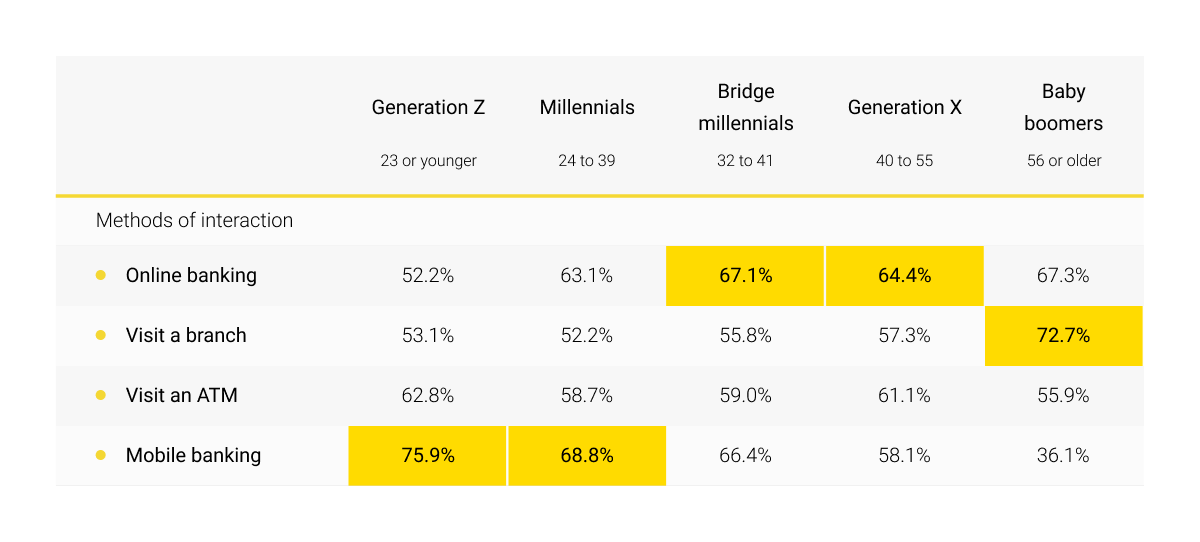
Along with conversational banking technology, tech implementation of virtual assistants may require such elements as underlying AI, enriched data, and visual components – as an out-of-the-box Software as a Service (SaaS) product. It is necessary to ensure the right level of integration of the virtual assistant with databases and platforms so that it has access to financial information and Big Data.
Services ensuring client security
Another personalization service on the client's part is a personalized cyber security system. It responds to non-typical login attempts or unusual financial transactions or transfers as compared to the preferences and typical activities of users. This enhances the capabilities of standard systems for personal data protection and account security.
The service can leverage the standard capabilities of a fraud detection system based on AI with additional training capabilities. Among the leaders in this market niche are such solutions as Shape Security, Darktrace, and Vectra, which are actively used in the banking sector.
How banks use personalized services
Data personalization services are in demand not only among clients. Technologies help financial institutions establish flexible personalized relationships with users and offer them the services they need. One of such personalization services in banking is assistance with making decisions about loan granting. The program collects information about the client, which makes the basis for an automatic recommendation to the banking service.
For example, the Zest Automated Machine Learning (ZAML) platform accumulates the personal information of clients, including “risky” ones, and forms their credit histories based on this information. As a result, banks are reducing their annual costs and increasing the likelihood of positive return forecasts.
Classical target marketing also belongs to personalization services. It helps service providers segment offers and sales through understanding the interests and preferences of selected consumer groups. Typically, these groups are formed by gender, age, social status, education, etc. Marketing tools for banks integrate with retail banking personalization services. As a result, clients find offers that appeal to them, while banks receive information for customizing their advertising and market strategies to target groups. This allows financial institutions to carry out micro-segmented marketing campaigns with better ROI.
A service called next best offering significantly contributes to the personalization of information about a client, their habits, preferences, and purchases. Systems like Next Best Action analytics software attract qualified leads by suggesting products and services they’d like and personalizing offers.
Personalization services and Big Data
What is needed for personalization services to work, taking into account their interaction with Big Data - information about user habits, behaviors, interests, and requests?
First of all, banks should introduce new approaches to data management. This includes the collection and unification of data from different sources, their standardization, and storage security, as well as interoperability when using various management systems.
Financial companies need to use specialized data storage such as data warehouses (to host structured datasets) and data lakes (to store large unstructured datasets and use them in the future). The key issues here are secure storage of and connection to data and the reduction of the risk of data loss or destructuring. Here, microservice architecture will help.
In order to manage data for personalization services in banking, the following data elements are required:
- Client expense structure and related transaction information;
- Data on financial services and products being used;
- Statistics and demographic data (CRM data) that indicate the individual preferences of a client based on their lifestyle.
Client-oriented approach
It is recommended for banks to consider the market strategy of a client-oriented approach. A client-centric goal set requires financial institutions to move beyond their traditional focus on product and service marketing, modernize analytics and technical services, retrain employees, and eliminate channel and offer silos.
Experts from BCG include the following components in it:
• Client DNA ensures a single view of each consumer based on data from various sources and dynamically reflects the state of a client at a given moment.
• A personalized curriculum helps to work out client solutions for a segment of one and determine the desired client behavior and incentive strategy.
• An analytics engine and recursive learning leverage Machine Learning and systematic experimentation to ensure flexibility of banking services and create personalized offers.
Practically, this is most often implemented through the creation of customer data platforms (CDPs). They bring together a complete history of client interactions and behavior across all communication channels, online and offline. This enables companies to provide consumers with a unified and multi-channel client experience.
Conclusion
Personalization of banking services is a demanded market trend nowadays. During the pandemic, the number of digital banking clients has increased, and this seems to be a sustained tendency.
According to surveys, almost all categories of clients welcome the personalization of services. Despite the fact that the level of confidence in banking services has dropped recently, its renewal and growth are achievable for most banks. This is largely possible with the development of appropriate personalization services.
Although most government regulators are concerned about the ethics, transparency, and security of AI-based services, all market players are sure that the development of these services is the future of the financial sector.
Personalization in banking presupposes that a financial institution knows its clients, understands their needs and wants, and orchestrates user data to meet them.
Personalization is not limited to the implementation of single services or components - it requires a systematic approach. This trend is implemented both on the client's side - through a personal consultant, virtual assistant, robo-advisor, virtual financial analyst, and personalized security service - and on the service provider's side - using a loan advisor, micro-segmented marketing service, and the next best offer analytics.
Personalization requires new approaches to data management, structuring, and storage. Banks also should create a client data orchestration system that includes client DNA, a personalized curriculum, and analytics and recursive learning engines. All this requires the development and implementation of new technologies and assistance from experienced FinTech partners so that financial institutions can overcome new challenges.